Introduction
Adhesive back magnets, particularly those prccoduced by 3M, are renowned for their exceptional adhesion properties and versatility in numerous applications, including signage, displays, and various industrial uses. To guarantee that these magnets function effectively, adhesion testing is critical. This article will delve deeper into the various adhesion testing methods, procedures, factors influencing adhesion strength, and the significance of these tests in ensuring product quality and performance.
Understanding 3M Adhesive Back Magnets
What Are 3M Adhesive Back Magnets?
3M adhesive back magnets are made from flexible magnetic materials coated with a high-performance adhesive on one side. This combination allows them to adhere securely to a range of surfaces, including metal, glass, plastic, and painted surfaces.
Types of 3M Adhesive Back Magnets
3M provides a variety of adhesive back magnets, each designed for specific applications:
- Flexible Magnets: These are ideal for applications requiring bending or shaping, such as refrigerator magnets or customizable signage.
- Magnetic Strips: Often used in retail environments for displays, these strips can be cut to size and applied easily.
- Die-Cut Magnets: Available in various shapes and sizes, die-cut magnets are suitable for specialized applications, including promotional materials.
- High-Temperature Magnets: Designed for applications subjected to extreme temperatures, these magnets maintain their adhesive properties even under challenging conditions.
Importance of Adhesion Testing
Adhesion testing evaluates the bonding strength of the adhesive to the substrate, ensuring the magnets perform effectively in their intended applications. The importance of this testing can be summarized as follows:
- Quality Assurance: Consistent testing helps maintain high product standards and ensures that each batch meets performance criteria.
- Performance Evaluation: By understanding the adhesion strength, manufacturers can predict how the magnets will perform over time and in various conditions.
- Product Development: Testing informs the design and formulation of new products, leading to continuous improvement.
- Compliance: Many industries have strict regulations regarding adhesive products; adherence to testing standards ensures compliance.
Adhesion Testing Methods
Various methods are used to assess the adhesion strength of 3M adhesive back magnets, each suited for different applications and conditions.
Peel Test
Overview
The peel test measures the force required to peel the adhesive away from a substrate at a specific angle. It simulates the conditions in which the adhesive bond may be subjected to forces attempting to separate the two surfaces.
Detailed Procedure
- Sample Preparation:
- Cut the adhesive back magnet to a standard size (e.g., 1 inch by 4 inches).
- Clean the substrate surface with an appropriate cleaner to remove any contaminants (e.g., dust, oil).
- Adhesive Application:
- Firmly press the adhesive back magnet onto the substrate using a roller or similar tool to ensure full contact and eliminate air bubbles.
- Follow the manufacturer’s recommended application pressure and dwell time.
- Conditioning:
- Allow the adhesive to cure according to 3M’s guidelines, which may include specific temperature and humidity conditions.
- A common practice is to let the sample cure for 24 hours at room temperature, but this can vary based on specific product requirements.
- Testing Setup:
- Utilize a tensile testing machine equipped with a peel test fixture.
- Set the peel angle to 90 degrees for standard peel testing.
- Measurement:
- Initiate the test by pulling the magnet away from the substrate at a constant rate (e.g., 12 inches per minute).
- Record the force required to peel the adhesive at different points along the test length.
- Data Analysis:
- Calculate the average peel strength in pounds per inch (lb/in) from multiple test samples.
- Analyze the results for any patterns indicating potential failure points or weaknesses.
Shear Test
Overview
The shear test assesses the adhesive bond strength by applying force parallel to the bonded surfaces, simulating conditions where lateral forces may act on the adhesive.
Detailed Procedure
- Sample Preparation:
- Cut the adhesive back magnet to a standard size, ensuring the adhesive layer is intact.
- Setup:
- Use a shear testing machine or fixture capable of applying a controlled horizontal force.
- Ensure the substrate is adequately prepared, clean, and free from contaminants.
- Adhesive Application:
- Apply the adhesive back magnet to the substrate, pressing it firmly to ensure full contact.
- Allow the adhesive to cure as per the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Testing:
- Attach the testing apparatus to the magnet so that the force is applied evenly across the bonded area.
- Gradually increase the load until the adhesive bond fails, either by cohesive failure (within the adhesive) or adhesive failure (at the interface).
- Measurement:
- Record the maximum force required to break the bond and calculate the shear strength using the formula:
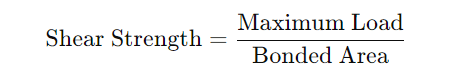
- Data Analysis:
- Analyze the results to determine average shear strength and assess performance against specifications.
Other Methods
- Dynamic Tensile Test:
- This test measures the adhesive’s performance under dynamic or fluctuating loads, mimicking real-world conditions such as vibration and movement.
- Environmental Testing:
- Evaluates how adhesion is affected by varying environmental conditions, including temperature extremes, humidity, and exposure to chemicals.
- Durability Testing:
- This involves subjecting the adhesive bonds to aging processes, such as temperature cycling, UV exposure, and moisture exposure, to assess long-term performance.
Industry Standards for Adhesion Testing
Adherence to industry standards during adhesion testing is crucial to ensure that products meet quality benchmarks. The following standards provide guidelines for conducting adhesion tests:
ASTM Standards
- ASTM D903: Standard Test Method for Peel or Stripping Strength of Adhesive Bonds.
- Specifies the procedure for measuring the peel strength of adhesive bonds, including sample preparation, testing apparatus, and calculation methods.
- ASTM D1002: Standard Test Method for Apparent Adhesion of Rigid Plastic and Metal to a Rigid Substrate.
- Details the procedures for shear strength testing, including sample preparation and environmental conditioning.
ISO Standards
- ISO 4624: Method for the determination of adhesion by pull-off testing.
- This standard focuses on evaluating adhesive bonds by measuring the force required to pull an adhesive layer away from a substrate.
- ISO 2409: Method for assessing the adhesion of coatings by tape test.
- While more commonly used for coatings, this method can provide insight into the adhesion of adhesive back magnets in specific applications.
Factors Affecting Adhesion
Understanding the factors that influence adhesion is essential for optimizing the performance of 3M adhesive back magnets.
Surface Preparation
Proper surface preparation is critical for achieving strong adhesion. Factors include:
- Cleanliness: Surfaces must be free from contaminants like dust, grease, and moisture. Pre-cleaning with solvents or detergents is often recommended.
- Surface Texture: Rougher surfaces may improve mechanical interlocking, while smooth surfaces might require different adhesive formulations to enhance bonding.
Environmental Conditions
Environmental factors during application and curing significantly impact adhesion strength:
- Temperature: The optimal temperature range for applying adhesives is typically specified by the manufacturer. Adhesives may not bond effectively in extreme temperatures, either too hot or too cold.
- Humidity: High humidity can affect the curing process and may result in weaker bonds. It is crucial to monitor humidity levels during application.
Adhesive Properties
The specific characteristics of the adhesive layer play a vital role in the overall performance:
- Initial Tack: The ability of the adhesive to adhere quickly upon contact is crucial for many applications. High tack is often desirable for immediate bonding.
- Curing Time: Different adhesives have varying cure times, which can affect the ultimate bond strength. Understanding the recommended cure time is essential for optimal performance.
Aging
Over time, the properties of adhesives can change due to environmental exposure and mechanical stress. Aging tests, such as exposure to UV light or extreme temperatures, help evaluate long-term performance and durability.
Case Studies
Case Study 1: Signage Application
A practical study was conducted on the adhesion of 3M adhesive back magnets used in outdoor signage. The testing included:
- Testing Method: Peel tests were conducted in varying conditions, including high humidity (90% RH) and extreme temperatures (-10°C to 50°C).
- Results: The adhesive maintained an average peel strength of 15 lb/in in normal conditions, with a slight reduction to 12 lb/in under high humidity, indicating adequate performance for most outdoor signage applications.
Case Study 2: Automotive Industry
An automotive manufacturer conducted shear strength tests on 3M adhesive back magnets used in car interior components.
- Testing Method: Shear tests were performed under both static and dynamic loading conditions.
- Results: The magnets exhibited shear strengths exceeding 30 lb/in² under static conditions, while dynamic testing revealed a slight decrease to 25 lb/in². The results validated the use of these magnets in critical automotive applications, ensuring reliability and safety.
Best Practices for Adhesion Testing
To achieve accurate and consistent results in adhesion testing, it is crucial to adhere to the following best practices:
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Always refer to the specific application instructions and adhesive recommendations provided by 3M to optimize results.
- Standardize Testing Conditions: Perform tests in controlled environments to minimize the impact of temperature, humidity, and other variables.
- Use Proper Equipment: Employ calibrated and appropriate testing machines, ensuring they are suited for the specific adhesion tests being conducted.
- Conduct Multiple Trials: To ensure the reliability of results, conduct multiple tests on different samples and average the results.
- Document Everything: Maintain comprehensive records of the testing process, including conditions, results, and any anomalies. This documentation is vital for quality control and regulatory compliance.
Conclusion
Adhesion testing of 3M adhesive back magnets is integral to ensuring product reliability and performance. Through various testing methods, such as peel and shear tests, manufacturers can gain valuable insights into the bonding strength and durability of these magnets. Adhering to industry standards and best practices enhances the testing process, ensuring that 3M adhesive back magnets meet or exceed customer expectations.
As technology advances, ongoing research and development in adhesive formulations will continue to enhance the performance of these magnets. Regular adhesion testing will remain essential in evaluating and validating their effectiveness in various applications, ultimately contributing to better product design and improved customer satisfaction. By prioritizing adhesion testing, businesses can ensure that they leverage the full potential of 3M adhesive back magnets in their respective industries, provide solutions that are not only effective but also reliable and long-lasting.