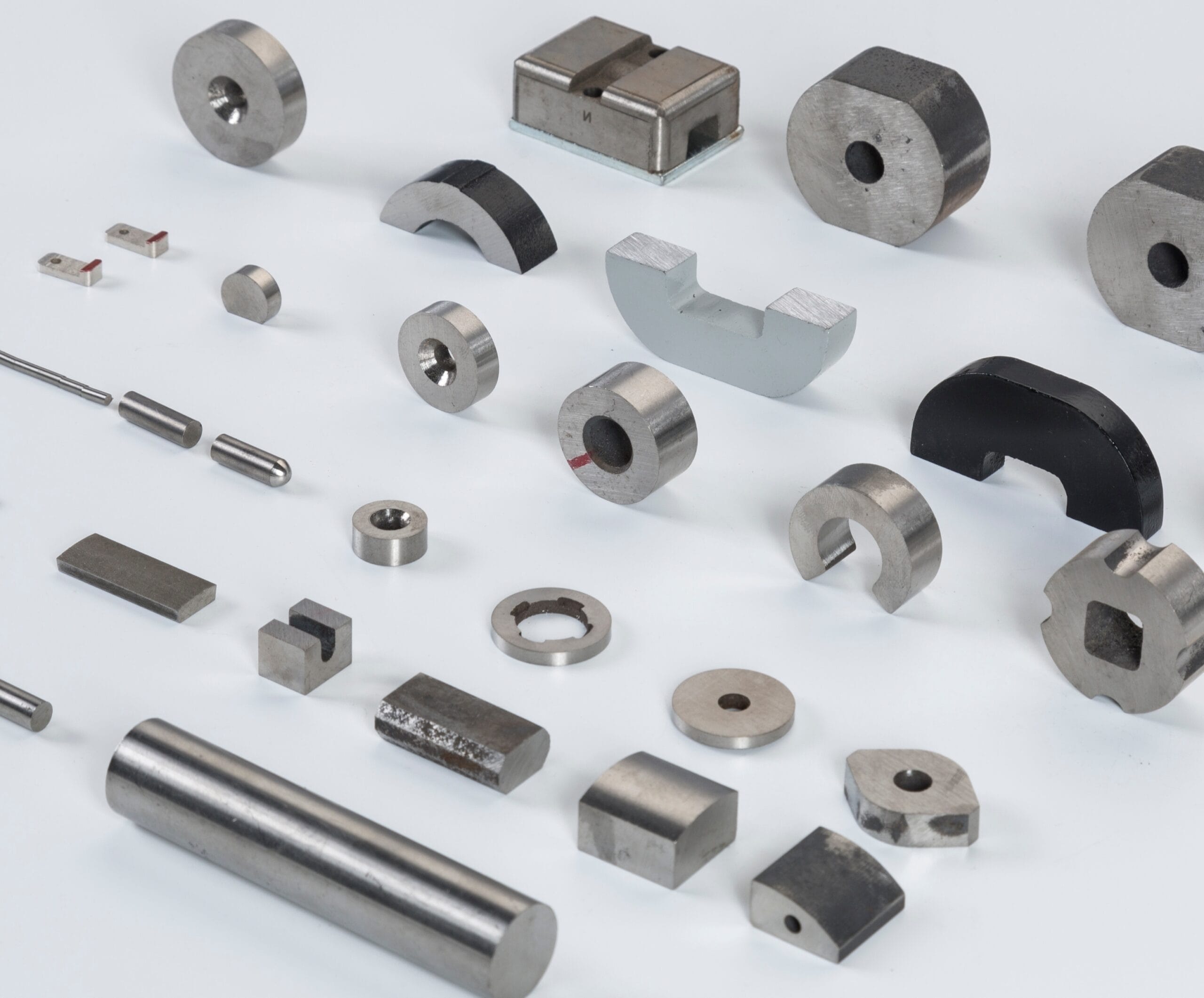
Introduction
Magnets, those seemingly simple yet fascinating objects, play a crucial role in our everyday lives. From powering the motors in our electric cars to enabling the speakers in our smartphones, magnets are integral to modern technology. But not all magnets are created equal. When it comes to high-performance applications, the debate often boils down to two main types: Alnico magnets and Rare Earth magnets. Each has its unique properties, advantages, and uses, making them indispensable in different contexts. So, what sets these magnets apart, and how do you choose the right one for your needs? Let’s dive into the intriguing world of magnets and unravel the differences and applications of Alnico and Rare Earth magnets.
1. Overview of Magnet Types
1.1. Brief History of Magnets
Magnets have a storied history dating back to ancient Greece, where the naturally occurring mineral magnetite was first discovered. These early “lodestones” exhibited magnetic properties that fascinated scientists and philosophers alike. Over the centuries, the understanding and application of magnets have evolved dramatically, leading to the development of various types of artificial magnets.
1.2. What are Alnico Magnets?
Alnico magnets are one of the oldest types of man-made magnets, first developed in the 1930s. Composed primarily of aluminum (Al), nickel (Ni), and cobalt (Co), along with iron and other elements, Alnico magnets were a revolutionary advancement in magnetic technology. Their ability to retain a strong magnetic field at high temperatures made them ideal for early industrial and automotive applications.
1.3. What are Rare Earth Magnets?
Rare Earth magnets are a more recent development, coming into prominence in the latter half of the 20th century. These magnets are made from rare earth elements, primarily Neodymium (NdFeB) and Samarium Cobalt (SmCo). Known for their exceptional strength, Rare Earth magnets have enabled advancements in technology that were previously unimaginable. Their high magnetic strength and resistance to demagnetization have made them essential in a wide range of high-tech applications.
2. Composition and Manufacturing
2.1. Alnico Magnets
Alnico magnets are composed of an alloy of aluminum, nickel, and cobalt, with iron as the primary element. Trace amounts of copper and titanium may also be added to improve the magnetic properties. The manufacturing process involves either casting or sintering. In casting, the molten alloy is poured into a mold and cooled, while sintering involves compacting the alloy powder and heating it until it forms a solid mass.
2.2. Rare Earth Magnets
Rare Earth magnets, specifically Neodymium and Samarium Cobalt, have complex compositions. Neodymium magnets are made from an alloy of neodymium, iron, and boron (NdFeB), while Samarium Cobalt magnets are made from samarium and cobalt (SmCo). The manufacturing process typically involves powder metallurgy. The alloy is melted and cooled to form a fine powder, which is then compressed in a magnetic field and sintered to create the final magnet.
3. Magnetic Properties
3.1. Alnico Magnets
Alnico magnets are known for their good magnetic strength and excellent temperature stability, withstanding temperatures up to 550°C. However, they have a lower coercivity, meaning they can be demagnetized more easily compared to Rare Earth magnets. This makes them suitable for applications where stability at high temperatures is critical, but not where extreme magnetic strength is required.
3.2. Rare Earth Magnets
Rare Earth magnets, particularly Neodymium, are the strongest type of permanent magnets available. They have high coercivity, meaning they retain their magnetic properties even under adverse conditions. Neodymium magnets are known for their strength but can be affected by high temperatures unless specifically engineered for thermal stability. Samarium Cobalt magnets, on the other hand, offer a balance of high magnetic strength and temperature resistance up to 300°C.
4. Applications
4.1. Common Uses of Alnico Magnets
Alnico magnets are widely used in applications that require stability at high temperatures. In the automotive industry, they are used in sensors and ignition systems. In the electronics sector, Alnico magnets are found in microphones, speakers, and other audio equipment. Industrial applications include use in motors, generators, and measuring instruments where consistent magnetic performance is necessary despite temperature fluctuations.
4.2. Common Uses of Rare Earth Magnets
Rare Earth magnets are crucial in high-performance applications. Neodymium magnets are used in electric motors for vehicles, wind turbines, and high-performance industrial machinery. They are also key components in consumer electronics such as hard drives, headphones, and smartphones. In the medical field, Rare Earth magnets are used in MRI machines and hearing aids, where their high magnetic strength and reliability are indispensable.
5. Advantages and Disadvantages
5.1. Alnico Magnets
*Advantages*:
– Excellent temperature stability
– Resistance to corrosion
– Easy to magnetize and demagnetize
*Disadvantages*:
– Lower magnetic strength compared to Rare Earth magnets
– Brittle and can break under mechanical stress
5.2. Rare Earth Magnets
*Advantages*:
– Extremely high magnetic strength
– High coercivity and resistance to demagnetization
– Versatility in various applications
*Disadvantages*:
– Higher cost due to rare earth element content
– Susceptibility to corrosion, requiring protective coatings
– Potential performance issues at very high temperatures (Neodymium)
6. Cost and Availability
6.1. Alnico Magnets
The cost of Alnico magnets is influenced by the prices of aluminum, nickel, and cobalt. While these materials are more common and less expensive than rare earth elements, the manufacturing process (casting or sintering) also impacts the final cost. Alnico magnets are generally more affordable and widely available, making them a cost-effective choice for many applications.
6.2. Rare Earth Magnets
Rare Earth magnets are more expensive due to the scarcity and high cost of rare earth elements like neodymium and samarium. The advanced manufacturing processes required to produce these magnets also contribute to their higher price. Despite their cost, the superior magnetic properties of Rare Earth magnets often justify the investment for high-performance applications. However, market availability can be affected by geopolitical factors and supply chain issues.
7. Environmental and Economic Considerations

7.1. Alnico Magnets
The production of Alnico magnets involves mining and processing of aluminum, nickel, and cobalt, which have environmental impacts, though generally less severe than those associated with rare earth mining. Economically, Alnico magnets are influenced by fluctuations in the prices of these metals, but they remain relatively stable and affordable.
7.2. Rare Earth Magnets
The extraction and processing of rare earth elements are environmentally intensive, often involving harmful chemicals and generating significant waste. Additionally, the majority of rare earth mining is concentrated in specific regions, leading to economic and geopolitical dependencies. Efforts are ongoing to improve the sustainability and efficiency of rare earth production, including recycling initiatives and research into alternative materials.
8. Future Trends and Innovations
8.1. Advances in Alnico Magnets
Research into improving the magnetic properties of Alnico magnets focuses on enhancing their strength and durability while maintaining temperature stability. Innovations may lead to new applications in industries that require reliable performance under extreme conditions. There is also potential for developing Alnico magnets with tailored properties for specific uses, expanding their versatility.
8.2. Advances in Rare Earth Magnets
Future trends in Rare Earth magnets include reducing dependency on rare earth elements through the development of new magnetic materials and improving recycling methods to reclaim rare earths from used devices. Innovations in manufacturing processes aim to enhance the thermal stability and corrosion resistance of Neodymium magnets, making them even more versatile. Research into composite materials and hybrid magnets may also open new possibilities for high-performance applications.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between Alnico and Rare Earth magnets is crucial for selecting the right type for your specific needs. While Alnico magnets offer excellent temperature stability and cost-effectiveness, Rare Earth magnets provide unmatched magnetic strength and versatility. By considering factors such as magnetic properties, cost, environmental impact, and future trends, you can make an informed decision that best suits your application. Magnets are more than just simple objects; they are the backbone of modern technology, driving innovation and enabling advancements across various industries.