Introduction
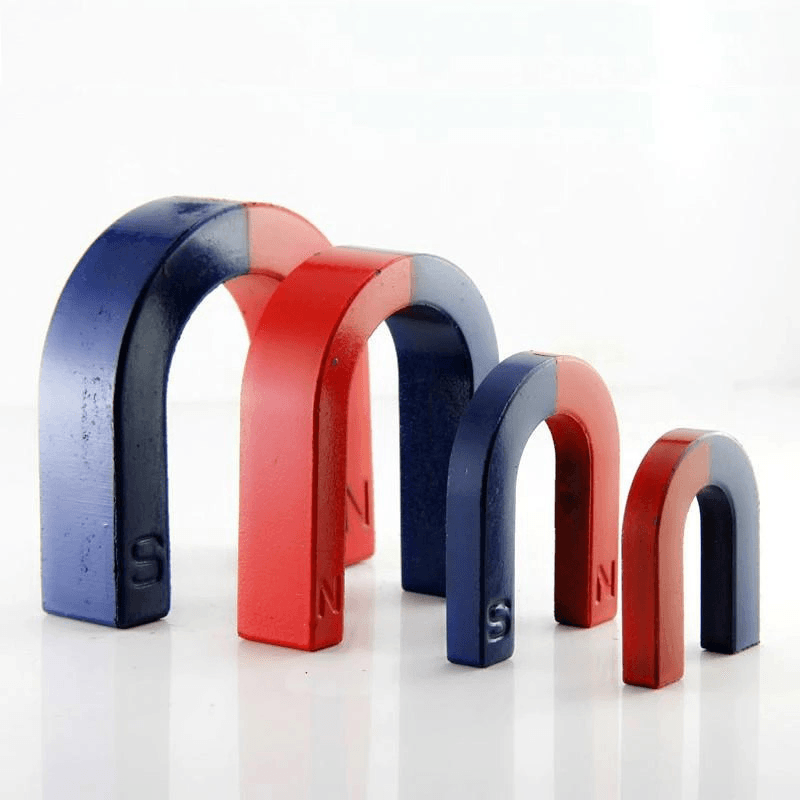
Ferrite education magnets are an essential tool in the field of education, particularly in science and engineering disciplines. These magnets, made from ferrite materials, are widely used in classrooms, laboratories, and educational kits to demonstrate fundamental principles of magnetism, electromagnetism, and material science. This article delves into the properties, applications, benefits, and educational significance of ferrite education magnets, providing a comprehensive understanding of their role in modern education.
What are Ferrite Magnets?
Ferrite magnets, also known as ceramic magnets, are composed of iron oxide (Fe₂O₃) combined with other metallic elements such as barium (Ba) or strontium (Sr). The chemical formula for ferrite is typically represented as MO·Fe₂O₃, where M is a divalent metal ion. These magnets are manufactured through a process called sintering, which involves compacting and heating the powdered ferrite material to form a solid mass.
Types of Ferrite Magnets
- Hard Ferrites: These are permanent magnets with high coercivity, meaning they retain their magnetization even in the presence of an external magnetic field. Hard ferrites are commonly used in educational magnets due to their durability and stability.
- Soft Ferrites: These materials have low coercivity and are easily magnetized and demagnetized. Soft ferrites are often used in applications requiring rapid changes in magnetization, such as in transformers and inductors.
Properties of Ferrite Magnets
Ferrite magnets possess several unique properties that make them ideal for educational purposes:
- High Magnetic Permeability: Ferrite magnets have a high magnetic permeability, allowing them to concentrate magnetic flux effectively. This property is crucial for demonstrating magnetic field lines and interactions.
- Electrical Insulation: Unlike metallic magnets, ferrite magnets are electrical insulators. This property prevents eddy currents, making them suitable for high-frequency applications and reducing energy losses.
- Temperature Stability: Ferrite magnets exhibit stable magnetic properties over a wide temperature range, ensuring consistent performance in various environmental conditions.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Ferrite magnets are relatively inexpensive to produce, making them an affordable option for educational institutions and students.
- Corrosion Resistance: Ferrite magnets are resistant to corrosion, ensuring longevity and reliability in educational settings.
Applications of Ferrite Education Magnets
Ferrite education magnets are versatile tools used in a wide range of educational applications. Some of the most common uses include:
1. Demonstrating Magnetic Fields
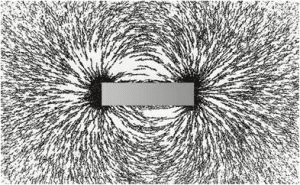
One of the primary uses of ferrite education magnets is to visualize and demonstrate magnetic fields. By placing a ferrite magnet under a sheet of paper and sprinkling iron filings on top, students can observe the magnetic field lines formed by the magnet. This hands-on experiment helps students understand the concept of magnetic flux and the direction of magnetic fields.
2. Exploring Magnetic Poles
Ferrite magnets are often used to teach students about magnetic poles—north and south. By bringing two ferrite magnets close to each other, students can observe the attractive and repulsive forces between like and unlike poles. This simple experiment reinforces the fundamental principle that opposite poles attract and like poles repel.
3. Building Electromagnetic Devices
Ferrite magnets are integral components in the construction of simple electromagnetic devices such as motors, generators, and speakers. In educational settings, students can use ferrite magnets to build basic electric motors, demonstrating the conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy. These projects provide a practical understanding of electromagnetism and its applications.
4. Studying Magnetic Materials
Ferrite magnets are also used to study the properties of different magnetic materials. By comparing ferrite magnets with other types of magnets (e.g., neodymium or alnico), students can learn about the differences in magnetic strength, coercivity, and temperature stability. This comparative analysis enhances students’ understanding of material science and the factors influencing magnetic performance.
5. Investigating Magnetic Levitation
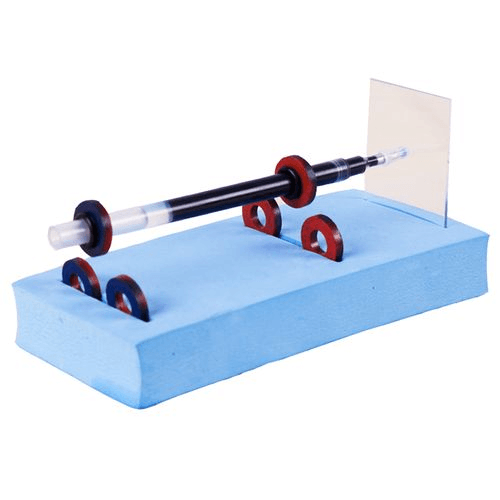
Ferrite magnets can be used to demonstrate the principles of magnetic levitation, where an object is suspended in the air using magnetic fields. This phenomenon is often showcased in educational kits that allow students to build simple magnetic levitation devices. Such experiments introduce students to advanced concepts like magnetic repulsion and the potential applications of magnetic levitation in transportation and engineering.
6. Exploring Magnetic Induction
Ferrite magnets are essential in experiments involving magnetic induction, where a changing magnetic field induces an electric current in a conductor. Students can use ferrite magnets to explore Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction by moving a magnet through a coil of wire and observing the generated current. This experiment is fundamental in understanding the principles of electricity generation and transformers.
Benefits of Using Ferrite Education Magnets
The use of ferrite education magnets offers several advantages in educational settings:
1. Hands-On Learning
Ferrite magnets provide a tangible way for students to interact with magnetic principles. Hands-on experiments and projects using ferrite magnets engage students in active learning, making abstract concepts more concrete and understandable.
2. Safety
Ferrite magnets are generally safe to handle, making them suitable for use in classrooms and laboratories. Unlike some high-strength magnets (e.g., neodymium magnets), ferrite magnets are less likely to cause injury or damage if mishandled.
3. Durability
Ferrite magnets are robust and resistant to wear and tear, ensuring they can withstand repeated use in educational environments. Their corrosion resistance further enhances their longevity, making them a cost-effective investment for schools and institutions.
4. Versatility
The versatility of ferrite magnets allows them to be used in a wide range of experiments and projects, from basic demonstrations to more complex applications. This adaptability makes them a valuable resource for educators teaching various levels of science and engineering.
5. Cost-Effectiveness
As mentioned earlier, ferrite magnets are relatively inexpensive compared to other types of magnets. This affordability makes them accessible to educational institutions with limited budgets, ensuring that students have the opportunity to engage with magnetic principles without significant financial constraints.
Educational Significance of Ferrite Magnets
Ferrite education magnets play a crucial role in fostering a deeper understanding of magnetism and its applications. Their use in classrooms and laboratories helps students develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and experimental skills. Here are some key educational benefits:
1. Foundation for Advanced Studies
Understanding the basics of magnetism is essential for students pursuing advanced studies in physics, engineering, and material science. Ferrite magnets provide a solid foundation for exploring more complex topics such as electromagnetism, quantum mechanics, and magnetic materials.
2. Encouraging Curiosity and Exploration
Hands-on experiments with ferrite magnets spark curiosity and encourage students to explore the natural world. By observing and manipulating magnetic fields, students develop a sense of wonder and a desire to learn more about the underlying principles of science.
3. Promoting STEM Education
Ferrite magnets are integral to STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) education. They provide practical, real-world applications of scientific concepts, helping students see the relevance of their studies in everyday life and future careers.
4. Enhancing Collaborative Learning
Many experiments involving ferrite magnets are conducted in groups, promoting collaborative learning and teamwork. Students work together to design experiments, analyze results, and draw conclusions, fostering communication and cooperation skills.
5. Bridging Theory and Practice
Ferrite magnets bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. By engaging in hands-on activities, students can see how theoretical concepts are applied in real-world scenarios, reinforcing their understanding and retention of the material.
Conclusion
Ferrite education magnets are invaluable tools in the realm of science and engineering education. Their unique properties, versatility, and cost-effectiveness make them ideal for a wide range of educational applications, from basic demonstrations to complex projects. By providing hands-on learning experiences, ferrite magnets help students develop a deeper understanding of magnetic principles and their practical applications. As educators continue to emphasize the importance of STEM education, ferrite magnets will remain a cornerstone of effective teaching and learning in the sciences. Whether used in a classroom, laboratory, or home setting, ferrite education magnets inspire curiosity, foster critical thinking, and pave the way for future innovations in science and technology.