Building a simple electric motor at home is not only an exciting and educational project but also a great way to introduce yourself to the basic principles of electromagnetism and motion. In this guide, I will show you how to make a homopolar motor, one of the simplest types of electric motors that you can build using common household materials. This motor operates based on the principle of magnetic fields interacting with electric currents, resulting in rotational motion. With just a few basic materials and some creativity, you can create your own electric motor. Let’s get started!
Safety Precautions
Before we dive into the project, it’s essential to keep safety in mind. While building this motor does not require advanced tools, there are some safety guidelines to follow to ensure a smooth and safe experience:
- Magnets Safety: Neodymium magnets are extremely strong and can pose a risk, especially for children. Keep magnets away from small children to avoid the danger of swallowing. Always supervise any young users closely.
- Avoid Large Magnets: Large magnets (those heavier than 1 oz) can pinch your fingers, causing injury. Stick with small, manageable magnets for safety.
- Battery Safety: If the motor does not rotate or if there is any unusual behavior, immediately disconnect the copper wire from the battery and magnets to prevent the battery from overheating or burning out.
- Work in a Safe Area: Since the motor will involve magnets and wires, work on a stable surface, free of distractions, and in a well-lit space.
With these safety measures in place, you’re ready to proceed with making your very own simple electric motor.
Materials You Will Need
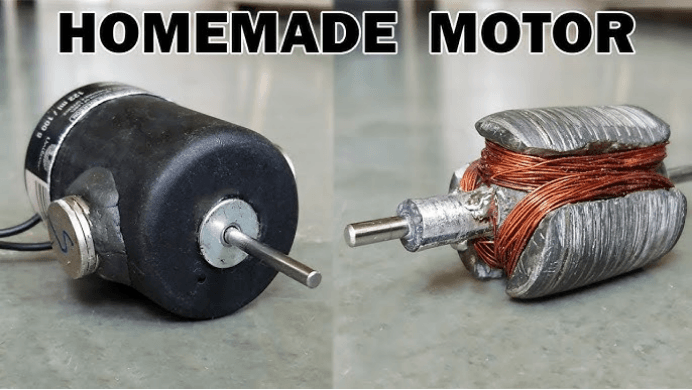
The materials required for this project are simple and easy to obtain. Here’s a list of everything you will need:
- Copper Wire (or Aluminum Wire): Copper is ideal because of its excellent conductivity, but aluminum wire will work as well. A thin gauge wire (like 22 AWG or similar) is best for flexibility and ease of bending.
- Neodymium Magnets: You will need at least two small, strong neodymium disc magnets. These are essential for creating the magnetic field that will interact with the electric current to generate motion.
- AA Battery: A fresh AA battery provides the right amount of power for the motor to run for an extended period. Ensure the battery is new or fully charged.
- Electrical Tape (optional): For securing the wire and magnets to the battery or other components.
- Scissors or Wire Cutters: Used for cutting and shaping the wire.
- Pliers: To help with bending and shaping the wire into the proper form.
These materials are easy to find around the house or at any local hardware store, and they don’t require any special skills or knowledge to use.
Step 1: Prepare the Materials
Start by gathering all the necessary materials. Ensure that you have a clean, flat surface to work on, as this will make the assembly process easier and more efficient. If you’re using wire cutters or scissors, ensure they are sharp and functional. Check that the battery is new or sufficiently charged.
Preparation of Copper Wire
Take a length of copper wire about 10 to 12 inches long. The wire needs to be long enough to form the motor’s arm, which will rotate around the battery. If you’re unsure of the length, start with a longer piece—you can always trim it down later.
Next, strip about half an inch of insulation from both ends of the copper wire using your wire cutters or scissors. This will expose the copper underneath, allowing the wire to make a good connection with the battery and the magnets.
Step 2: Shape the Copper Wire
This is where the creative part begins! The copper wire will form the structure of the motor’s arm. To create a simple yet effective design, bend the copper wire into an oval or loop shape. The oval shape allows the wire to sit around the battery while also being able to make contact with the magnets.
Tips for Shaping the Wire:
- Bend it Carefully: Use your fingers or pliers to bend the wire gently. Aim for a symmetrical oval shape that fits snugly around the battery.
- Smooth the Ends: Ensure that the two ends of the copper wire are smooth and make a good electrical connection with the battery terminals and magnets. You may need to slightly bend the ends to touch the battery and magnets securely.
- Create Balanced Symmetry: For optimal motor function, make sure both ends of the wire are the same length, as an uneven design can cause imbalance and prevent smooth rotation.
Step 3: Attach the Magnets to the Battery
To start the motor, you’ll need to set up the magnets correctly. Begin by attaching the neodymium magnets to the positive terminal of the AA battery.
- Position the Magnets: Place one magnet directly on the positive end of the battery. This magnet will serve as the interaction point for the electric current in the wire.
- Secure the Magnets: You can use a small piece of electrical tape to secure the magnets in place. However, this is optional—magnets will often stick to the battery on their own due to their strong magnetic field.
Next, take the second magnet and attach it to the negative terminal of the battery. This will complete the magnetic circuit, allowing the wire to interact with the magnetic field.
Step 4: Attach the Copper Wire to the Battery
Now that the magnets are in place, it’s time to attach the copper wire to the battery. Carefully position the copper wire so that both ends of the wire are touching the battery terminals (one end will touch the positive terminal, and the other will touch the negative terminal through the magnet).
Key Considerations for Wiring:
- Ensure Good Contact: Both ends of the copper wire must make solid contact with the battery terminals and magnets for the current to flow properly.
- Test for Movement: Gently nudge the wire to see if the motor begins to rotate. The wire should move in a circular motion around the battery, creating the motor’s desired rotational effect.
Step 5: Watch the Motor Spin
Once the wire is in place and the circuit is complete, the motor should begin to spin. The interaction between the electric current flowing through the copper wire and the magnetic field created by the neodymium magnets generates a force known as the Lorentz force, which is what causes the wire to rotate.
- Adjust the Wire Position: If the motor isn’t spinning right away, try adjusting the position of the wire slightly. It may take a little fine-tuning to get the motor running smoothly.
- Observe the Motor’s Motion: As the electric current flows through the wire, it will experience a force perpendicular to both the current and the magnetic field. This results in the wire spinning around the battery, creating motion.
Troubleshooting Tips
If your motor isn’t working as expected, try these troubleshooting tips:
- Check the Wire Connections: Ensure that the wire is securely attached to the battery and magnets. A loose connection can prevent the motor from spinning.
- Test the Battery: Ensure the battery is properly charged. A weak battery may not provide enough power for the motor to function.
- Recheck Magnet Positioning: If the magnets are too far from the battery terminals, the magnetic field may not be strong enough to generate sufficient motion.
Step 6: Customization and Experimentation
Now that you’ve built a simple homopolar motor, you can experiment with different designs and modifications to improve or customize your motor. Here are a few ideas:
- Different Wire Shapes: Experiment with different wire shapes, such as a spiral or a star shape, to see how it affects the motor’s speed and stability.
- Add More Magnets: Try adding more magnets to the system to see if the motor’s speed increases or if it becomes more powerful.
- Use Larger Batteries: For more power and longer runtime, experiment with larger batteries such as C or D cells. Just make sure to adjust your design accordingly to fit the larger size.
Conclusion
Making a simple electric motor at home is a fun and educational project that introduces you to basic concepts in electricity and magnetism. By following the steps outlined above, you can build your own homopolar motor with just a few simple materials. With some creativity and experimentation, you can modify and improve your motor design for even greater fun and learning.
Enjoy your DIY electric motor project, and feel free to share your creative variations and improvements!