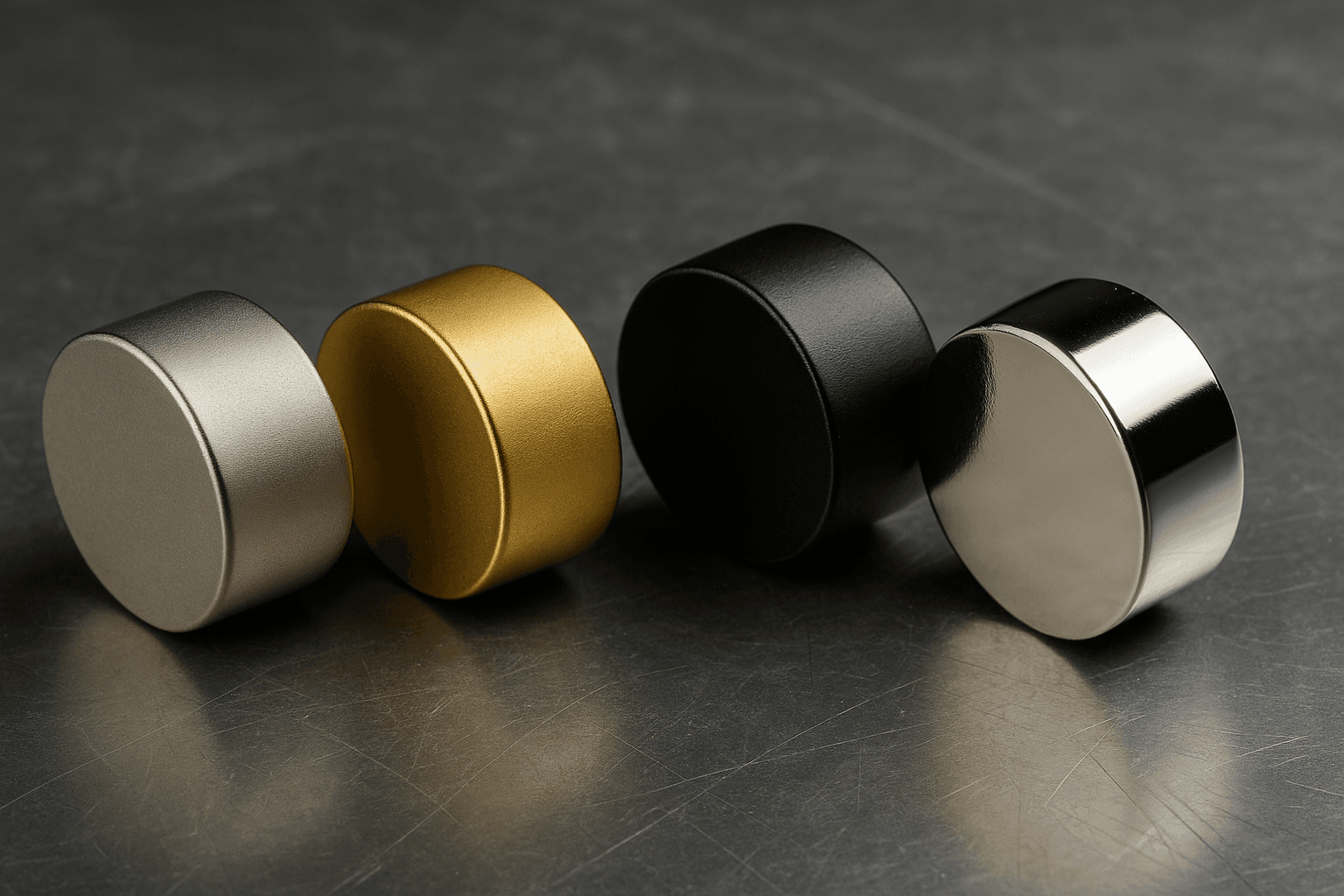
Permanent magnets—especially high-performance NdFeB (Neodymium-Iron-Boron)—are central to modern motors, robotics, automation, aerospace, renewable energy, medical devices, and sensing systems. However, sintered NdFeB suffers from inherent vulnerabilities: chemical reactivity, moisture sensitivity, structural brittleness, and weak grain-boundary strength. These weak points make protective coatings an essential part of any magnet engineering or application design.
Coatings determine whether a magnet lasts for years or fails within months, especially in environments involving humidity, abrasion, salt, chemicals, or thermal cycling. This guide provides a deep engineering analysis of how to choose the best coating for corrosion protection, mechanical wear resistance, high-humidity stability, and application-specific reliability.
1. Why NdFeB Magnets Require Coatings
1.1 Structural and chemical vulnerability of NdFeB
NdFeB magnets are produced via powder metallurgy, resulting in a microstructure with:
- Iron-rich grain boundaries
- High porosity
- Electrochemical reactivity
- Poor ductility and tensile strength
- Low fracture toughness
Moisture and oxygen attack grain boundaries first, leading to structural swelling, surface blistering, and rapid degradation.
1.2 Corrosion begins at edges, cracks, and defects
Coating failure rarely begins at smooth surfaces. Instead, it is triggered at:
- Sharp corners
- Thinly coated edges
- Machined surfaces
- Handling scratches
- Pinholes in plating
- Micro-cracks from assembly impact
Once initiated, corrosion propagates beneath the coating, often expanding unseen until catastrophic failure occurs.
1.3 Coatings provide more than corrosion protection
Coatings also contribute:
- Increased surface hardness
- Enhanced wear resistance
- Chemical shielding
- Electrical insulation
- Biocompatibility
- Improved thermal cycling tolerance
- Reduced friction (in PTFE-type coatings)
- Dampening of mechanical shock
Therefore, coating selection must consider both environmental conditions and mechanical interface requirements.
2. Engineering Overview of Magnet Coating Options
This section analyzes each coating’s behavior, mechanical performance, chemical stability, failure mechanisms, and industrial suitability.
2.1 NiCuNi (Nickel–Copper–Nickel)
Corrosion behavior
NiCuNi provides moderate corrosion resistance but is vulnerable in:
- High humidity
- Salt spray
- Chloride environments
- Repetitive condensation cycles
Moisture penetrates through pinholes or compromised edges, leading to copper layer corrosion and coating lift.
Mechanical performance
- High surface hardness
- Excellent abrasion resistance
- Uniform thin coating (~12–25 μm)
- Best option for tight air-gap motors
Failure modes
- Edge cracking under impact
- Delamination due to poor substrate preparation
- Sub-film corrosion initiated at defects
- Surface blistering under hydrogen accumulation
Best for
Motors, rotors, robotic actuators, high-speed applications, magnetic rings, Halbach arrays, and environments where mechanical strength matters most.
2.2 Epoxy Coating (Black, Grey, and Custom Colors)
Corrosion behavior
Outstanding moisture protection due to organic polymer barrier:
- Excellent salt spray resistance
- Excellent humidity cycling stability
- Strong chemical resistance
Epoxy is ideal for environments where NiCuNi alone fails.
Mechanical performance
- Softer coating
- High impact cushioning
- Poor abrasion resistance
- Sensitive to sharp metal contact
- Scratches expose porous NdFeB immediately
Failure modes
- Surface scratching → rapid under-film corrosion
- UV-induced aging
- Thermal embrittlement above ~120°C
- Thin corners due to flow characteristics during coating
Best for
Outdoor devices, security equipment, marine sensors, renewable energy components, HVAC controls, and devices requiring long-term corrosion durability.
2.3 Zinc Coating

Corrosion behavior
Provides short-term, sacrificial protection.
However:
- White rust forms quickly
- Weak under high humidity
- Not suitable for long-term outdoor use
Mechanical performance
Soft, easily scratched, not recommended for wear-intensive applications.
Best for
Low-cost consumer electronics and temporary applications.
2.4 Phosphate Coating
Performance
Phosphate is not a corrosion coating; it is an interface treatment used for:
- Enhancing adhesive bonding
- Improving resin wetting
- Promoting adhesion in overmolding
- Reducing friction during assembly
Best for
Bonded NdFeB magnets, ferrite magnets, and components that will be embedded in resin or polymer matrices.
2.5 PTFE / Everlube / Teflon Coating

Corrosion behavior
Moderate. PTFE itself is chemically inert, but the underlying bond layers determine long-term corrosion resistance.
Mechanical performance
- Extremely low coefficient of friction
- Excellent sliding wear resistance
- Good chemical stability
- Not suitable for impact or abrasion
Best for
Linear motion stages, valves, robotics, dynamic applications where friction reduction is critical.
2.6 Gold Coating
Corrosion behavior
Gold is fully inert against oxidation and most chemical environments.
Mechanical performance
- Very thin (~0.5–1 μm)
- Soft and easily scratched
- Requires Ni underlayer for adhesion
Best for
Bio-sensing devices, medical instruments, wearables, cleanroom systems, and miniaturized precision magnets.
2.7 Parylene (C / N / F)
Corrosion behavior
Parylene is a CVD-applied, completely conformal, pinhole-free barrier with:
- Extremely low moisture permeability
- Uniform thickness even on complex geometries
- Excellent chemical resistance
Mechanical performance
- Flexible
- Electrically insulating
- Not abrasion-resistant unless enclosed in housings
Best for
Underwater sensors, hermetically sealed assemblies, medical systems, aerospace components, and long-lifecycle high-reliability devices.
3. Understanding Magnet Failure Mechanisms
Coating choice must be informed by the most common field failures.
3.1 Edge-initiated corrosion
Edges have the thinnest coating and the highest mechanical stress.
Mitigation
- Chamfer edges
- Thicker epoxy formulations
- Parylene conformal coverage
- Multi-layer systems (NiCuNi + Epoxy)
3.2 Sub-film corrosion spreading
Once corrosion penetrates coating defects, it spreads laterally.
Mitigation
- Epoxy (slows diffusion)
- Parylene (blocks moisture)
- Hybrid systems for redundancy
3.3 Mechanical cracking and chipping
NdFeB cracks easily under:
- Press-fit assembly
- Rotor installation
- Impact
- Vibration
Mitigation
- NiCuNi for mechanical stiffness
- Epoxy for impact cushioning
- Protective housings
3.4 Chemical degradation
Lubricants, coolants, acids, or solvents degrade certain coatings.
Mitigation
- PTFE for chemical resistance
- Parylene for high-purity chemical shielding
- Epoxy for mild chemical exposure
3.5 Thermal cycling fatigue
Different thermal expansion rates cause coating stress.
Mitigation
- Parylene (best flexibility)
- Epoxy for moderate conditions
- NiCuNi only for stable temperature environments
4. Selection Framework for Corrosion, Wear, and Humidity Conditions
Here is a practical engineering-based method for choosing the correct coating.
4.1 High-Humidity or Condensation-Prone Environments
Recommended coatings
- Epoxy
- NiCuNi + Epoxy
- Parylene C
Rationale
Epoxy and Parylene dramatically reduce moisture diffusion and eliminate pinhole-driven failure.
4.2 Marine or Salt-Spray Environments
Recommended coatings
- Epoxy (economical)
- Parylene C (premium)
- Hybrid NiCuNi + Epoxy
Rationale
Nickel alone fails quickly in chloride environments.
4.3 Wear, Abrasion, or Sliding Interfaces
Recommended
- NiCuNi
- PTFE
- Hard nickel
Avoid
Epoxy in dynamic interfaces due to poor abrasion resistance.
4.4 Medical, Wearable, or Biocompatible Applications
Recommended coatings
- Parylene C
- Gold plating
- Medical-grade epoxy
Rationale
These coatings provide biocompatibility, chemical inertness, and low irritation.
4.5 High-Temperature Applications
Material first, coating second
Use:
- High-temperature NdFeB (SH–EH grades)
- SmCo magnets for >200°C
Coatings
- NiCuNi
- Phosphate (for bonded magnets)
5. Validation Methods for Coating Quality
5.1 Salt Spray Testing (ASTM B117)
Tests the onset and progression of:
- Pitting
- Sub-film corrosion
- Blistering
- Edge degradation
5.2 Adhesion Tests
- Cross-hatch adhesion
- Pull-off tests
- Impact and chipping tests
- Centrifugal adhesion tests for rotors
5.3 Coating Thickness Measurement
Using:
- XRF
- Eddy current gauges
- SEM cross-sections
Tight thickness control is essential for high-speed motors.
5.4 Environmental Cycling
- Temperature cycling
- Humidity cycling
- UV exposure
- Chemical compatibility tests
- Abrasion resistance tests
6. Final Selection Summary
If corrosion resistance is top priority:
→ Epoxy or Parylene C
If mechanical wear resistance is essential:
→ NiCuNi or PTFE
If both corrosion and wear matter:
→ NiCuNi + Epoxy hybrid
If biocompatibility is required:
→ Parylene C or Gold
If exposed to salt spray:
→ Avoid NiCuNi alone → use Epoxy or Parylene
If for high-speed rotors:
→ NiCuNi