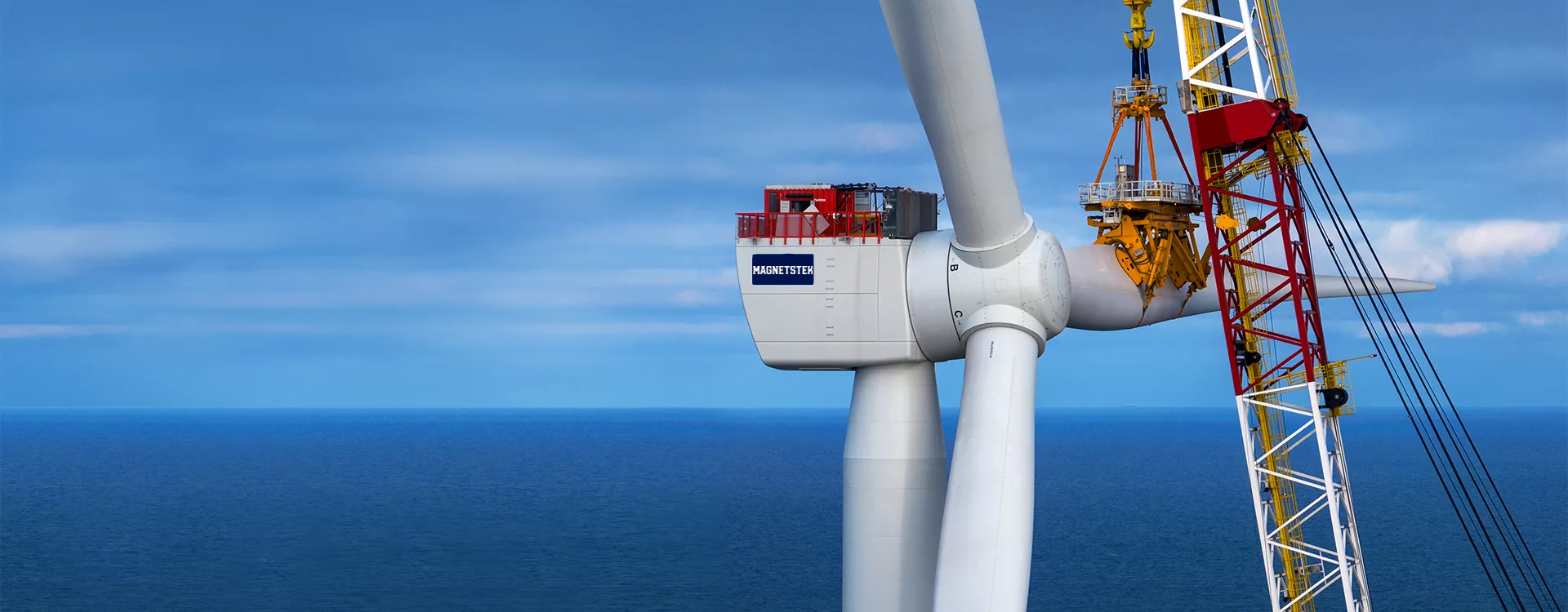
Magnets play a crucial role in the functioning of rotors and motors. They are used in various electric motors, such as permanent magnet and induction motors. The main applications of magnets in rotors and motors include:
- Permanent Magnet Motors: These motors use permanent magnets for field excitation and a wound armature. The permanent magnets can be made of neodymium, samarium-cobalt, ferrite, aluminum nickel cobalt, and strontium carbonate-iron oxide (ceramic magnet). Permanent magnet motors are used in variable-speed drives, where the stator is supplied from a variable-frequency, variable-voltage, electronically controlled source. They are highly efficient and capable of precise speed and position control.
- Electric Vehicles: Permanent magnet motors are used in electric vehicles like GM’s Chevrolet Bolt. These motors are versatile, highly efficient, and available in AC and DC varieties.
- Pumps, Fans, Blowers, and Grinders: Permanent magnet AC motors have a simplified rotor that enables higher efficiency with small torque loads and high-speed capabilities. They are used in various applications, including pumps, fans, blowers, grinders, mixers, and conveyors.
- Computer Drives and Household Items: Permanent magnet DC motors are used in computer drives, household items such as electric toothbrushes and vacuum cleaners, operating windshield wipers and heater blowers in automobiles, and electric tools such as drills and hedge trimmers.
- Medical and Aerospace Applications: Neodymium iron boron magnets are used in size-sensitive applications, such as medical and aerospace, due to their high magnetic strength and compact size.
In summary, magnets play a vital role in rotors and motors, enabling efficient and reliable operation in various applications. They are used in permanent magnet motors, electric vehicles, pumps, fans, blowers, grinders, computer drives, household items, and medical and aerospace applications.
Post Views: 876