Introduction
The global push for sustainability has placed recycling at the forefront of efforts to conserve resources, reduce waste, and lower environmental impact. Recycling is no longer a mere option but a necessity for industries ranging from automotive to electronics. However, the efficiency of recycling processes hinges on advanced technologies that ensure high material purity and effective resource recovery. One such crucial tool is the Magnetic Separator, which plays an indispensable role in separating ferrous materials from non-ferrous waste streams.
Magnetic separators have revolutionized recycling by enabling the extraction of valuable metals and enhancing the overall quality of recycled products. From metal recovery in electronics to the removal of contaminants in plastic recycling, these devices have made a significant impact on how industries approach waste management. In this article, we will explore how magnetic separators work, the various types available, their applications in different recycling sectors, and the environmental and economic benefits they bring.
The Growing Importance of Recycling in Modern Industry
As the demand for sustainable practices increases, industries are shifting towards more eco-friendly approaches to waste management. Recycling has become a critical method for conserving resources, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and cutting down on landfill waste. The challenge, however, lies in effectively processing large quantities of recyclable material, particularly in separating metals from other waste streams.
The Magnetic Separator has emerged as an essential tool in modern recycling operations, providing an efficient solution for recovering ferrous metals from mixed materials. Whether it’s in large industrial plants or smaller recycling centers, magnetic separators have helped streamline recycling processes by making metal extraction faster, more efficient, and cost-effective.
How Magnetic Separators Work
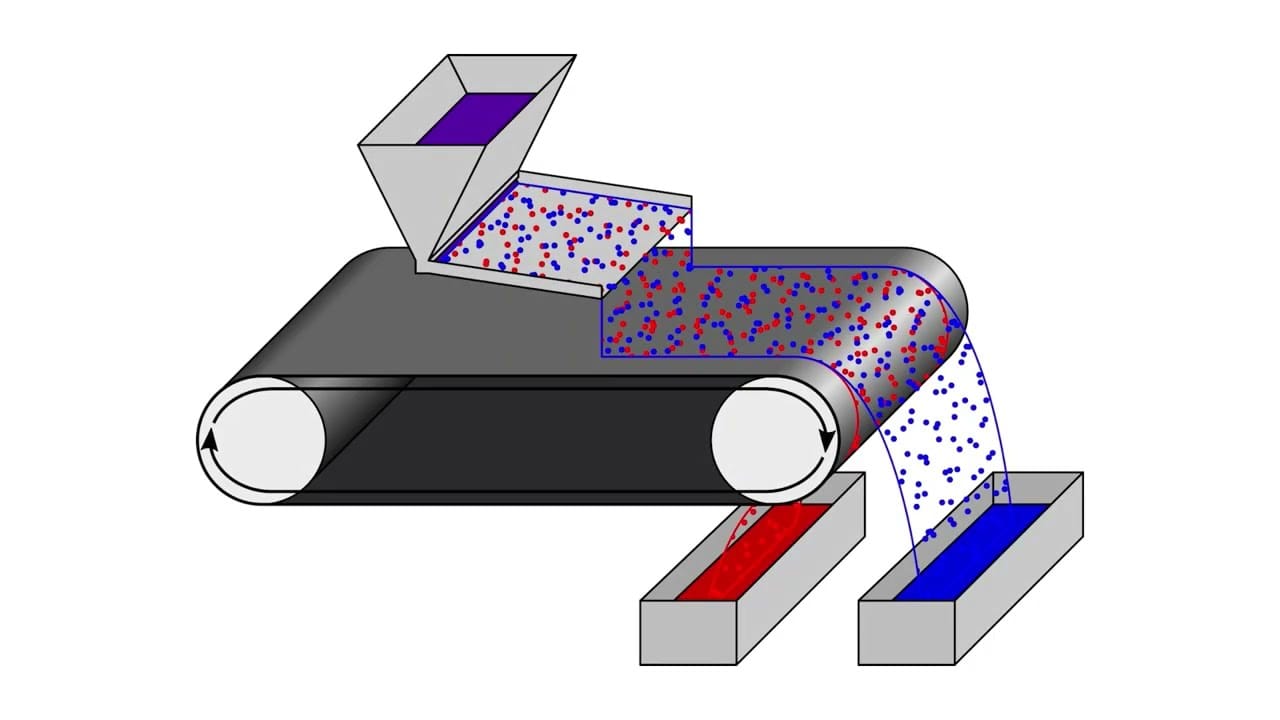
The Magnetic Separator is designed to remove ferrous materials, such as iron, from a waste stream by using a strong magnetic field. When materials are passed through the separator, ferrous particles are attracted to the magnetic surface, separating them from non-ferrous materials like plastic, glass, or paper. The separated metals are then collected for further processing, while the purified non-metallic materials continue through the recycling stream.
These separators vary in design, with some using a rotating magnetic drum and others positioned over conveyor belts. Despite these differences, the goal remains the same: to increase the purity of recycled materials and recover valuable metals that can be reused.
Types of Magnetic Separators
Magnetic separators come in a variety of types, each tailored to different material streams and specific recycling requirements. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types used in the industry:
1. Drum Magnetic Separators
Drum Magnetic Separators consist of a rotating drum with a magnetic core. As waste materials pass through the drum, ferrous metals are captured by the magnet and separated from non-metallic materials. This type is commonly used in metal recycling to efficiently recover ferrous scrap from non-metal materials.
2. Overbelt Magnetic Separators
Designed for heavy-duty applications, Overbelt Magnetic Separators are installed above conveyor belts to remove large ferrous materials, such as steel scraps or metal parts. These separators are ideal for large-scale operations and industries where bulky, high-volume waste needs to be processed.
3. Eddy Current Separators
Although not magnetic in the traditional sense, Eddy Current Separators are often paired with magnetic separators to recover non-ferrous metals like aluminum and copper. They work by inducing eddy currents that repel non-ferrous metals from other waste, allowing them to be sorted efficiently.
4. Plate Magnets
Plate Magnets are flat, rectangular magnets that are placed above conveyors to capture smaller ferrous contaminants. They are effective in industries where fine metal particles, such as in food or pharmaceuticals, need to be removed from other materials.
5. Crossbelt Magnetic Separators
Crossbelt Magnetic Separators are installed diagonally across conveyor belts. As materials pass underneath, the magnetic field captures ferrous metals and removes them from the stream. These separators are especially useful in automotive and construction recycling, where larger metal parts are common.
Applications of Magnetic Separators in Recycling
Magnetic separators have widespread applications in the recycling sector, serving various industries to ensure that metal recovery is efficient and the end materials are of high quality. Below are some of the key areas where magnetic separators are used:
1. Metal Recycling
Metal recycling is perhaps the most obvious application of Magnetic Separators. By recovering ferrous metals, such as iron and steel, from mixed waste streams, these separators play a crucial role in recycling facilities, helping to conserve natural resources and reduce the environmental impact of mining.
2. Electronics Recycling
The surge in electronic waste (e-waste) has made recycling electronic components a priority. Magnetic separators assist in recovering valuable metals like steel and copper from electronic devices, which can be reprocessed into new products.
3. Construction and Demolition Recycling
In the construction industry, where metal debris from building materials is common, Magnetic Separators help efficiently separate steel and iron from rubble. This not only conserves landfill space but also allows these metals to be reused in future construction projects.
4. Automotive Recycling
When vehicles reach the end of their lifecycle, they are dismantled and recycled. Magnetic Separators are used to recover valuable metals from old cars, including ferrous materials that can be re-melted and repurposed in new vehicles.
5. Plastic Recycling
In plastic recycling, ferrous contaminants can degrade the quality of the final recycled product. Magnetic separators ensure that plastics are free of metal particles, resulting in cleaner, high-quality recycled materials.
Environmental and Economic Benefits of Magnetic Separators
The use of Magnetic Separators in recycling not only helps recover valuable metals but also has profound environmental and economic benefits. Here are some key advantages:
1. Conservation of Resources
Magnetic separators allow metals to be recovered and reused, reducing the need for raw material extraction. This is particularly important in industries like electronics, where precious metals are involved.
2. Reduction in Landfill Waste
By efficiently extracting metals, magnetic separators help reduce the volume of waste sent to landfills, contributing to cleaner environmental practices.
3. Cost Savings
Recycling operations that use magnetic separators benefit from lower operational costs due to increased efficiency in metal recovery. This also translates into potential revenue streams from the sale of recovered metals.
4. Higher Quality Recycled Materials
By ensuring that ferrous contaminants are removed, magnetic separators improve the overall quality of recycled materials, making them more valuable and suitable for a wide range of applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, magnetic separators are a fundamental part of the recycling process, driving improvements in both environmental sustainability and operational efficiency. By separating ferrous materials from non-ferrous waste streams, these machines enable the recovery of valuable metals and ensure the production of high-quality recycled materials.
As industries increasingly adopt sustainable practices, the role of magnetic separators will continue to grow. Whether in metal, electronics, construction, automotive, or plastic recycling, these devices are key to reducing waste, conserving resources, and creating a more sustainable future.