Introduction
Magnet wire, also known as winding wire or coil wire, is a specialized type of insulated wire used in the construction of various electrical components, such as motors, transformers, and inductors. This wire plays a crucial role in the efficient operation of these devices, and understanding its properties, characteristics, and standards is essential for anyone working in the electrical or electronics industry.
What is Magnet Wire?
Magnet wire is a copper or aluminum conductor that is coated with a thin layer of insulating material, typically enamel, polyester, or polyamide. This insulation serves two primary purposes: it prevents electrical shorts between adjacent turns of the wire in a coil or winding, and it protects the conductor from environmental factors such as moisture, chemicals, and abrasion.
The insulation used on magnet wire is designed to withstand high temperatures and voltages, making it suitable for use in applications where these conditions are present. The thickness and type of insulation used depend on the specific requirements of the application, such as operating temperature, voltage, and environmental conditions.
Characteristics of Magnet Wire
Magnet wire is characterized by several key features that make it suitable for its intended applications:
1. Insulation Material: The insulation material used on magnet wire is a critical factor in determining its performance and suitability for specific applications. Common insulation materials include enamel, polyester, polyamide, and fiberglass, each with its own unique properties and advantages.
Enamel Insulation: Enamel insulation is one of the most widely used materials for magnet wire. It provides excellent electrical insulation and resistance to high temperatures, typically up to 200°C. Enamel-insulated wire is commonly used in motors, transformers, and other electrical components.
Polyester Insulation: Polyester insulation offers superior resistance to solvents, chemicals, and moisture compared to enamel insulation. It is often used in applications where these environmental factors are present, such as in automotive and aerospace industries. Polyester-insulated wire can withstand temperatures up to 180°C.
Polyamide (Nylon) Insulation**: Polyamide insulation provides excellent mechanical strength and resistance to abrasion, making it suitable for use in applications where the wire is subjected to vibration or movement. It can withstand temperatures up to 220°C.
Fiberglass Insulation**: Fiberglass insulation offers superior heat resistance and electrical insulation properties. It is commonly used in high-temperature applications, such as in furnaces and ovens, where temperatures can reach up to 450°C.
2. **Insulation Thickness**: The thickness of the insulation layer is carefully controlled to ensure proper electrical insulation and mechanical protection while minimizing the overall wire diameter. Thicker insulation provides better insulation but increases the wire’s overall size and weight.
3. Temperature Rating: Magnet wire is rated for specific temperature ranges, depending on the insulation material used. Enamel-insulated wire is typically rated for temperatures up to 200°C, while polyester and polyamide insulations can withstand higher temperatures, up to 250°C or more.
4. **Voltage Rating**: The insulation thickness and material also determine the voltage rating of the magnet wire. Higher voltage applications require thicker insulation to prevent electrical breakdown and short circuits.
5. **Mechanical Strength**: The insulation material and its thickness contribute to the overall mechanical strength of the magnet wire. Wires with polyamide or fiberglass insulation offer superior resistance to abrasion and vibration, making them suitable for applications where mechanical stress is a concern.
6. **Flexibility**: Magnet wire must be flexible enough to be wound into coils or windings without damaging the insulation or conductor. The insulation material and its thickness play a role in determining the wire’s flexibility.
7. **Conductor Material**: While copper is the most common conductor material used in magnet wire, aluminum is also used in some applications where weight is a critical factor. Aluminum conductors offer a lower weight-to-conductivity ratio compared to copper, but they are more susceptible to oxidation and have a higher resistance.
8. **Conductor Shape**: Magnet wire is typically available in round, rectangular, or square cross-sections. Round wires are the most common, but rectangular and square wires can be used in applications where space is limited or specific winding patterns are required.
Standards for Magnet Wire
To ensure consistent quality, performance, and safety, magnet wire is subject to various industry standards and specifications. These standards define the requirements for materials, dimensions, testing methods, and performance criteria. Some of the most widely recognized standards for magnet wire include:
1. **NEMA MW 1000**: This standard, published by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), covers the specifications for round, rectangular, and square magnet wire with various insulation materials, including enamel, polyester, polyamide, and fiberglass. It defines the requirements for conductor materials, insulation materials, insulation thickness, temperature ratings, voltage ratings, and mechanical properties.
2. **IEC 60317**: The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standard IEC 60317 specifies the requirements for insulated round winding wires used in electrical equipment. It covers a wide range of insulation materials, including enamel, polyester, polyamide, and fiberglass, and defines the requirements for dimensions, temperature ratings, voltage ratings, and testing methods.
3. **ASTM B173**: The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) standard B173 covers the specifications for copper and copper-alloy round wire for electrical purposes, including magnet wire. It defines the requirements for conductor materials, dimensions, and mechanical properties.
4. **UL 1446**: Underwriters Laboratories (UL) standard 1446 covers the requirements for insulated magnet wire used in electrical appliances and equipment. It specifies the requirements for insulation materials, insulation thickness, temperature ratings, voltage ratings, and testing methods.
5. **CSA C22.2 No. 187**: The Canadian Standards Association (CSA) standard C22.2 No. 187 specifies the requirements for insulated magnet wire used in electrical equipment. It covers a wide range of insulation materials and defines the requirements for dimensions, temperature ratings, voltage ratings, and testing methods.
These standards cover various aspects of magnet wire, including conductor materials, insulation materials, insulation thickness, temperature ratings, voltage ratings, mechanical properties, and testing methods. Compliance with these standards ensures that magnet wire meets the necessary performance and safety requirements for its intended applications.
Manufacturers of magnet wire must adhere to these standards to ensure consistent quality and performance, while users and specifiers of magnet wire can refer to these standards to select the appropriate wire for their specific applications.
Testing and Quality Control
To ensure that magnet wire meets the required specifications and standards, various testing and quality control measures are implemented throughout the manufacturing process. These tests are designed to evaluate the wire’s electrical, mechanical, and thermal properties, as well as its conformance to dimensional and material requirements.
1. **Electrical Testing**: Electrical tests are performed to evaluate the insulation resistance, dielectric strength, and voltage breakdown characteristics of the magnet wire. These tests ensure that the insulation can withstand the intended operating voltages and prevent electrical shorts or failures.
2. **Mechanical Testing**: Mechanical tests, such as tensile strength, elongation, and abrasion resistance, are conducted to assess the wire’s ability to withstand physical stresses and deformations during winding, handling, and operation.
3. **Thermal Testing**: Thermal tests, including heat aging and thermal endurance tests, are performed to evaluate the wire’s performance and insulation integrity at elevated temperatures. These tests ensure that the wire can withstand the intended operating temperatures without degradation or failure.
4. **Dimensional Inspection**: Dimensional inspections are carried out to verify that the wire’s conductor diameter, insulation thickness, and overall diameter conform to the specified tolerances and requirements.
5. **Material Analysis**: Material analysis techniques, such as spectroscopy and chemical analysis, are used to verify the composition and purity of the conductor and insulation materials, ensuring compliance with the specified standards.
6. **Sampling and Lot Testing**: Sampling and lot testing procedures are implemented to ensure that each production batch or lot of magnet wire meets the required quality standards. Statistical sampling methods are used to select representative samples for testing, and the results are used to accept or reject the entire lot.
7. **Continuous Monitoring**: During the manufacturing process, continuous monitoring and control systems are employed to track and adjust various parameters, such as insulation thickness, curing temperatures, and line speeds, to maintain consistent quality and minimize variations.
These testing and quality control measures are essential for ensuring the reliability and performance of magnet wire in critical applications, such as motors, transformers, and other electrical components. By adhering to strict quality standards and testing protocols, manufacturers can provide customers with high-quality magnet wire that meets or exceeds their requirements.
Applications of Magnet Wire
Magnet wire is used in a wide range of applications across various industries, including:
**Motors**: Magnet wire is an essential component in the construction of electric motors, where it is used to wind the stator and rotor coils. The insulation on the wire prevents electrical shorts and allows for efficient energy transfer. Motors are used in countless applications, from household appliances and power tools to industrial machinery and electric vehicles.
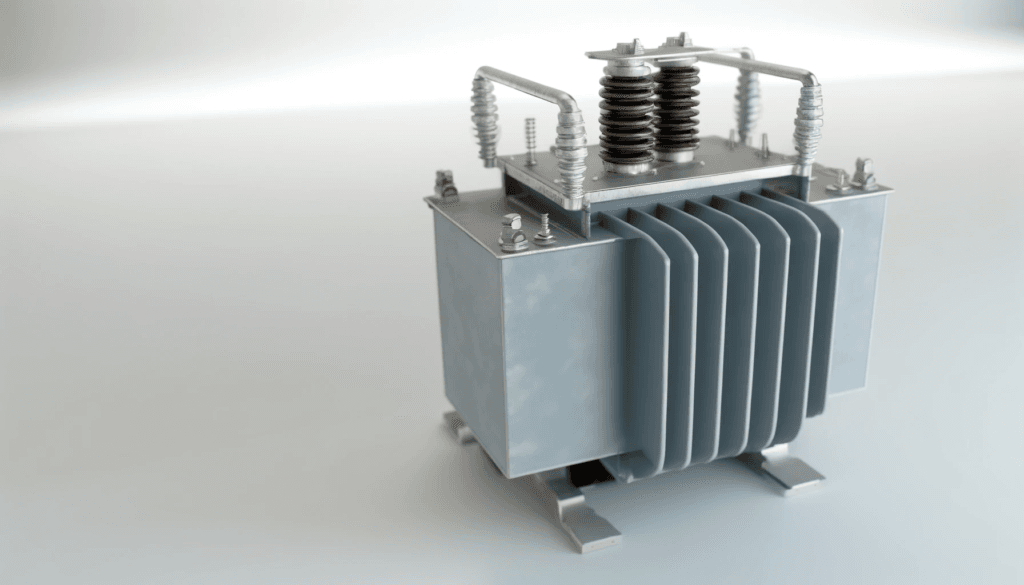
2. **Transformers**: Transformers rely on magnet wire to wind their primary and secondary coils. The insulation on the wire ensures proper electrical isolation between the coils and prevents short circuits. Transformers are crucial components in power distribution systems, electronics, and various industrial applications.
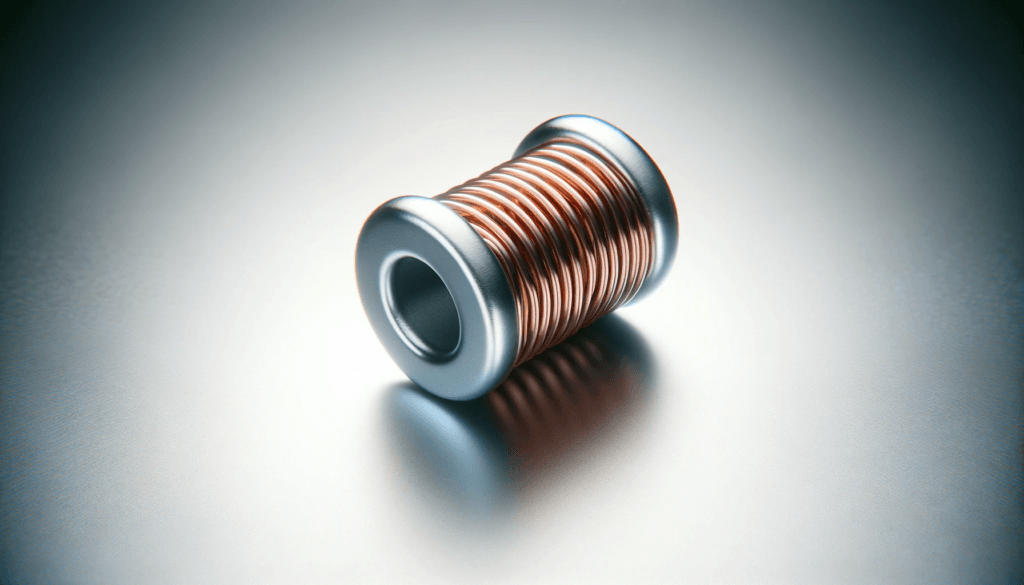

3. **Inductors**: Magnet wire is used to wind the coils in inductors, which are essential components in electronic circuits for filtering, energy storage, and signal processing. Inductors are found in a wide range of electronic devices, from radios and televisions to computers and telecommunication equipment.
4. **Relays and Solenoids**: These electromagnetic devices use magnet wire to create the magnetic fields necessary for their operation. Relays and solenoids are used in various applications, such as control systems, automotive components, and industrial automation.
5. **Generators and Alternators**: Magnet wire is used in the windings of generators and alternators, which convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. These devices are essential components in power generation systems, from large-scale power plants to small-scale renewable energy systems.
6. **Sensors and Actuators**: Various types of sensors and actuators, such as position sensors and linear actuators, utilize magnet wire in their construction. These devices are used in a wide range of applications, including industrial automation, robotics, and automotive systems.
7. **Medical Equipment**: Magnet wire is used in the construction of various medical devices, such as MRI machines, X-ray equipment, and therapeutic devices, where high-quality insulation and electrical performance are critical.
8. **Aerospace and Defense**: The aerospace and defense industries rely on magnet wire for various applications, including aircraft electronics, avionics systems, and military equipment, where reliability and performance under extreme conditions are paramount.
By understanding the characteristics and standards of magnet wire, engineers and technicians can ensure the proper selection and use of this critical component for their specific applications, contributing to the reliability and performance of electrical systems across a wide range of industries.

One Reply to “The Unsung Hero: How Magnet Wire Powers Our World”
Pretty! This has been an extremely wonderful article.
Many thanks for providing these details.
My page: website