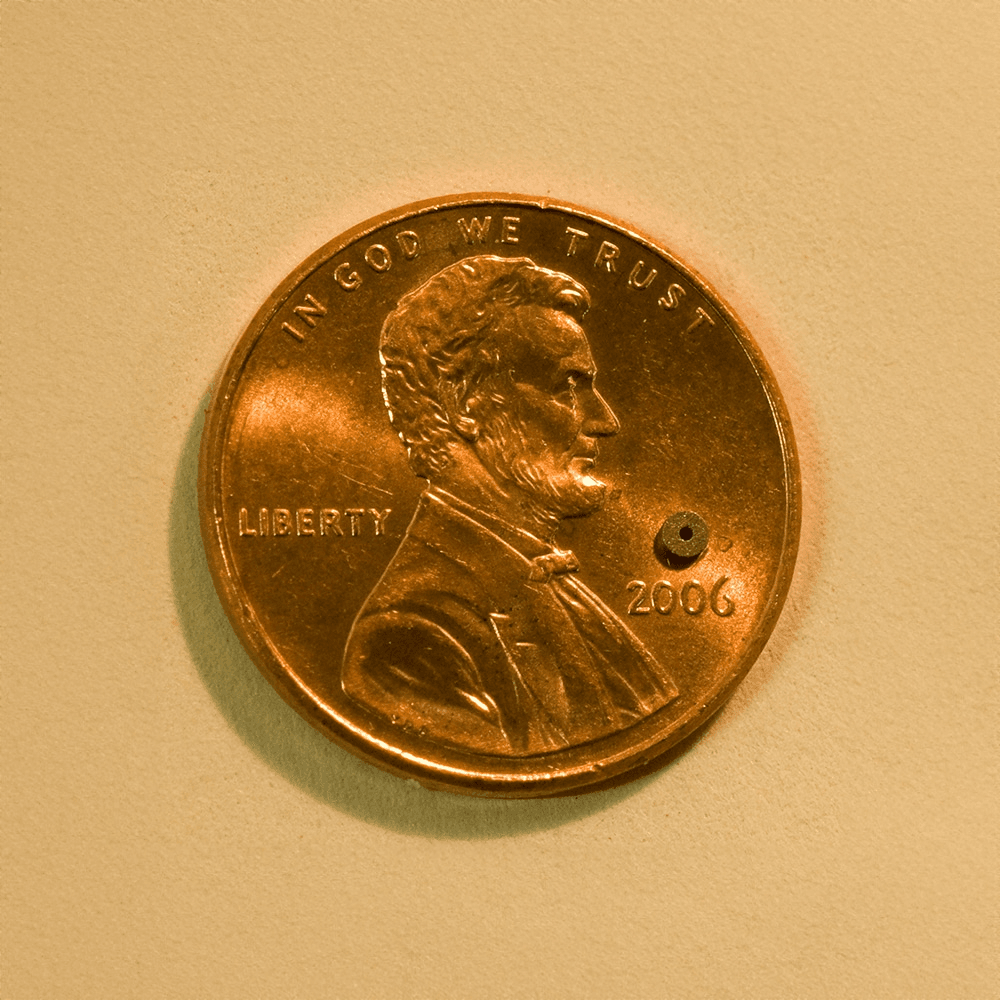Introduction
Tiny magnets, or micro magnets, are a fascinating component of modern technology and science. These small yet powerful magnetic elements have transformed a multitude of industries by offering precise magnetic fields in compact forms. From everyday consumer products to cutting-edge scientific instruments, tiny magnets play an essential role in enhancing functionality and performance. This article will explore the different types of tiny magnets, their applications, and how they impact various fields.
What Are Tiny Magnets?
Tiny magnets are magnetic components characterized by their small size, typically ranging from millimeters to micrometers. Despite their diminutive dimensions, these magnets possess strong magnetic properties and are designed to meet specific requirements for different applications. They are commonly used in a variety of technological, industrial, and consumer products due to their unique combination of size and magnetic strength.
Types of Tiny Magnets
Tiny magnets come in various types, each with distinct properties and applications. Understanding these types is crucial for leveraging their capabilities effectively.
Permanent Tiny Magnets
Permanent tiny magnets are made from materials that naturally retain their magnetic properties over time without the need for external power. These magnets are created using materials such as neodymium, samarium-cobalt, or ceramic ferrites. Permanent tiny magnets are renowned for their strength and durability, making them suitable for applications where a constant magnetic field is required.
Neodymium Magnets: Neodymium magnets are a type of rare earth magnet known for their exceptional strength. Despite their small size, they can generate a powerful magnetic field, making them ideal for high-performance applications. They are commonly used in hard drives, small motors, and magnetic assemblies.
Samarium-Cobalt Magnets: These magnets are another type of rare earth magnet, known for their high magnetic strength and resistance to high temperatures. They are used in applications that require stability in extreme conditions, such as aerospace and military technologies.
Ceramic Ferrites: Ceramic ferrites are made from a combination of iron oxide and other metallic elements. They are less expensive than rare earth magnets and are commonly used in applications like refrigerator magnets and low-cost sensors.
Temporary Tiny Magnets
Temporary tiny magnets are materials that exhibit magnetic properties only when exposed to an external magnetic field. Once the external field is removed, these materials lose their magnetism. Temporary magnets are often made from soft iron or similar materials and are used in applications where temporary magnetism is needed.
Soft Iron Magnets: Soft iron is commonly used in temporary magnets due to its ability to easily magnetize and demagnetize. These magnets are used in devices like electromagnets and magnetic shielding, where the ability to switch the magnetic field on and off is essential.
Electromagnets
Electromagnets are created by passing an electric current through a coil of wire wrapped around a ferromagnetic core. The resulting magnetic field can be turned on or off and adjusted by varying the current. Electromagnets are highly versatile and are used in various applications that require control over the magnetic field.
Solenoids: A solenoid is a type of electromagnet used to convert electrical energy into linear motion. It is commonly used in valves, relays, and actuators.
Magnetic Cranes: Electromagnets are used in cranes to lift and move heavy ferromagnetic materials. The ability to control the magnetic field allows for precise handling of loads.
The Smallest Possible Magnets
The search for the smallest possible magnets is a cutting-edge area of research in nanotechnology. Scientists and engineers are developing nano-magnets, which are magnetic particles or structures on the scale of nanometers (billionths of a meter). These ultra-small magnets offer unique properties and applications.
Nano-Magnets: Nano-magnets are used in advanced technologies such as quantum computing and nanomedicine. They are crucial for creating highly sensitive magnetic sensors and for manipulating individual atoms and molecules.
Quantum Computing: Nano-magnets are used to study and manipulate qubits, the fundamental units of quantum information. Their precise magnetic fields are essential for controlling quantum states and performing quantum computations.
Nanomedicine: In nanomedicine, nano-magnets are employed for targeted drug delivery. They can be used to guide medications to specific locations within the body, improving treatment efficacy and minimizing side effects.
Applications of Tiny Magnets
Tiny magnets have a wide range of applications across various industries. Their small size and strong magnetic properties make them suitable for numerous uses, including:
Electronics
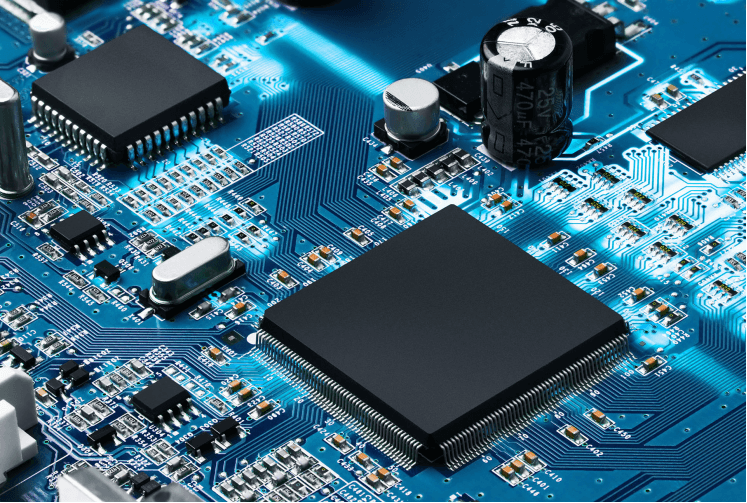
Tiny magnets play a crucial role in the electronics industry. Their compact size and strong magnetic fields are essential for various electronic components and devices.
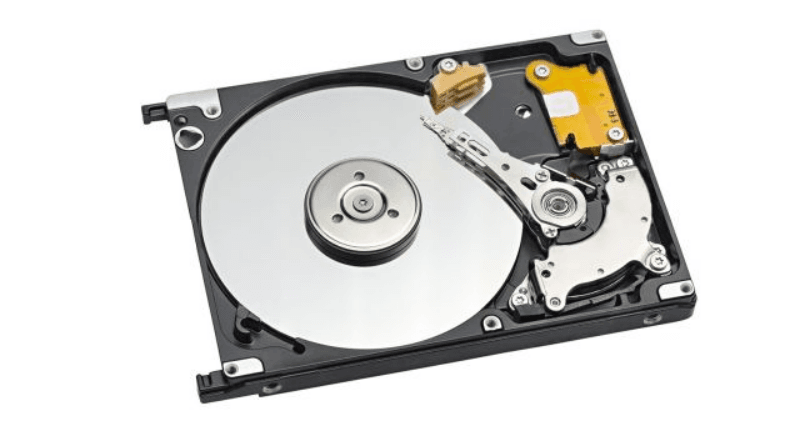

Hard Drives: In hard disk drives (HDDs), tiny magnets are used in the read/write heads to read and write data on the magnetic disk. Neodymium magnets are particularly valued for their strength and reliability in these applications.
Microactuators: Microactuators are miniature devices that use tiny magnets to produce motion or force. They are used in applications such as optical imaging systems, microfluidic devices, and miniature robots.
Sensors: Tiny magnets are used in magnetic sensors that detect changes in magnetic fields. These sensors are found in devices like smartphones, compasses, and proximity sensors.
Medical Devices
In the medical field, tiny magnets are utilized in various diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Their precise magnetic properties are essential for enhancing medical technologies.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Tiny magnets are used in MRI systems to produce high-resolution images of the body’s internal structures. Their magnetic fields help generate detailed images, aiding in diagnosis and treatment planning.
Drug Delivery Systems: Tiny magnets are employed in targeted drug delivery systems, where they help guide medications to specific areas within the body. This approach improves treatment accuracy and reduces side effects.
Medical Implants: Micro magnets are used in miniaturized medical implants that require precise control and operation. They are found in devices such as pacemakers and hearing aids.
Consumer Goods
Tiny magnets are commonly used in everyday consumer products. Their small size and strong magnetic properties make them ideal for various applications.
Refrigerator Magnets: Tiny magnets are used in refrigerator magnets to hold notes, pictures, and decorations on metal surfaces. Their compact size allows for a wide range of designs and uses.
Magnetic Closures: Magnetic closures are used in handbags, wallets, and other accessories to provide a secure and convenient fastening mechanism. Tiny magnets are chosen for their strength and durability.
Toys: Many small toys incorporate tiny magnets for interactive features. For example, magnetic building blocks and puzzles use tiny magnets to connect and assemble pieces.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, tiny magnets are used in various components and systems to improve vehicle performance and reliability.
Sensors: Tiny magnets are used in automotive sensors to monitor and control various systems, such as engine performance, tire pressure, and stability control.
Actuators: Micro magnets are used in actuators that control functions like electronic throttle control and adjustable mirrors. Their small size and strong magnetic fields allow for precise control.
Electronic Components: Tiny magnets are employed in electronic components such as ignition systems and fuel injectors. They contribute to the overall efficiency and reliability of automotive systems.
Aerospace and Defense
Tiny magnets are integral to aerospace and defense technologies, where precision and reliability are paramount.
Navigation Systems: In aerospace applications, tiny magnets are used in navigation systems to provide accurate positioning and orientation data. They are crucial for satellite guidance and aircraft control.
Satellite Components: Tiny magnets are used in satellite components to manage and control various functions, including attitude control and payload positioning.
Advanced Sensors: In defense applications, tiny magnets are used in advanced sensors that detect and measure magnetic fields. These sensors play a role in surveillance, targeting, and navigation.
Research and Development
Tiny magnets are employed in scientific research and development to explore magnetic properties and interactions at a microscopic level.
Materials Science: Researchers use tiny magnets to study the magnetic properties of materials and develop new materials with enhanced magnetic characteristics.
Physics: In physics research, tiny magnets are used in experiments to investigate fundamental magnetic interactions and phenomena.
Engineering: Engineers use tiny magnets in experimental setups and prototypes to test and refine new technologies and devices.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite their many applications, tiny magnets face several challenges and limitations. Some of the key challenges include:
Manufacturing Precision: Producing tiny magnets with consistent quality and performance requires advanced manufacturing techniques and equipment. Ensuring precise dimensions and magnetic properties can be challenging.
Material Limitations: The choice of materials for tiny magnets affects their performance and suitability for specific applications. Researchers are continuously exploring new materials and compositions to improve magnetic properties.
Integration: Integrating tiny magnets into complex systems and devices can be challenging due to their small size and the need for precise alignment and positioning.
Looking to the future, advancements in nanotechnology and materials science are expected to drive further developments in tiny magnets. Emerging technologies, such as quantum computing and advanced medical devices, will continue to rely on tiny magnets for their unique properties and capabilities.
Conclusion
Tiny magnets, or micro magnets, are small but powerful components that have a significant impact across various industries and applications. From electronics and medical devices to consumer goods and aerospace technologies, these magnets offer remarkable versatility and functionality. By understanding the different types of tiny magnets and their applications, we gain insight into the crucial role they play in advancing technology and improving everyday life.
For more information about tiny magnets and their applications, visit MagnetsTek’s Micro Magnets page.