In the invisible dance of forces that shape our world, magnets play a leading role, unseen yet fundamental. From guiding explorers with the humble compass to driving the futuristic propulsion of maglev trains, the spectrum of magnetic marvels is vast. Amidst this diversity, two types of magnets stand out for their distinct characteristics and applications: the powerful neodymium magnet and the ubiquitous regular magnet. The curiosity to understand their differences opens a window into the complex world of magnetism and its myriad applications in modern life.
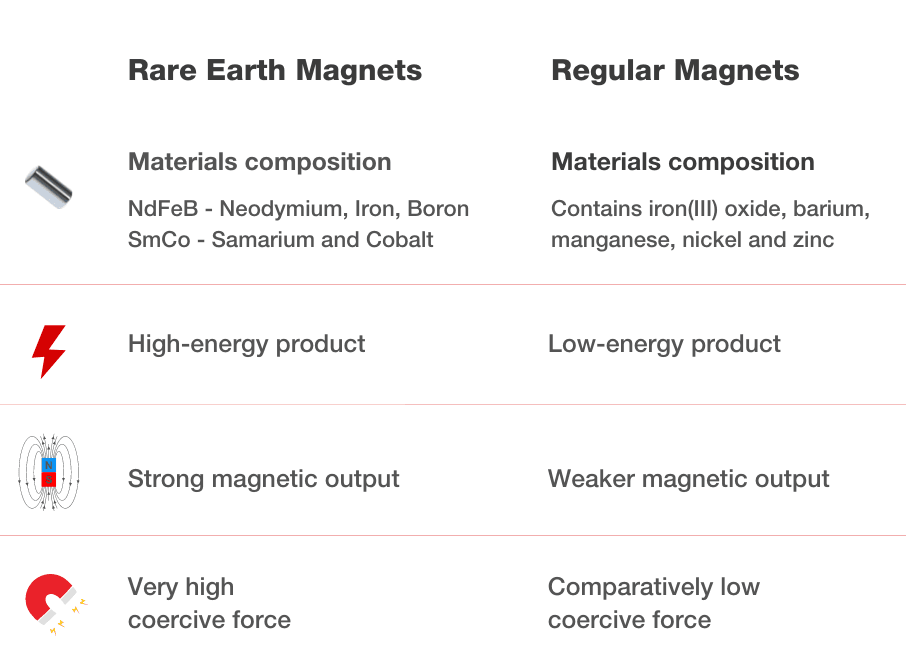
Neodymium magnets, composed of neodymium, iron, and boron, are the most potent permanent magnets, essential for advanced technologies and renewable energy. These rare earth magnets enable diverse high-tech applications due to their exceptional strength. In contrast, ferrite or ceramic regular magnets, made from iron oxide and carbonates, serve everyday needs with moderate strength, durability, and cost-efficiency. Despite being weaker, they are preferred for low-tech applications due to their resilience and affordability, marking a clear distinction in utility and performance between the two.
Introduction
Magnets are not just the objects sticking to our fridges or the tools we used in school science projects; they are integral to the functionality of modern technology and industrial machinery. Among the myriad types of magnets available, neodymium magnets and regular magnets (often ferrite or ceramic magnets) are two of the most widely used. Each type serves distinct purposes across various sectors, owing to their unique properties and capabilities.
What Are Neodymium Magnets?
Neodymium magnets, part of the rare-earth magnet family, are composed of neodymium, iron, and boron (NdFeB). Discovered in the 1980s, these magnets are renowned for their exceptional magnetic strength, making them the strongest permanent magnets available. Neodymium magnets exhibit a high magnetic field for their size, offering unparalleled performance in applications where space and weight are critical. However, they are sensitive to temperature changes and can corrode if not properly coated. They play crucial roles in technologies such as hard disk drives, electric motors in hybrid and electric vehicles, MRI machines, and various renewable energy technologies.
What Are Regular Magnets?
When we refer to “regular magnets,” we’re typically discussing ferrite or ceramic magnets. These are made from a mixture of iron oxide and strontium carbonate. Although they possess a lower magnetic force compared to neodymium magnets, ferrite magnets are not without their advantages. They offer excellent resistance to demagnetization and corrosion, perform well under high temperatures, and are cost-effective. These properties make them suitable for a wide range of applications, including in speakers, magnetic therapy products, motors, and as educational tools.
Key Differences Between Neodymium and Regular Magnets
Magnetic Strength and Field: Neodymium magnets are significantly stronger than ferrite magnets. This allows for smaller, more efficient designs in applications requiring strong magnetic fields.
Temperature Resistance: Ferrite magnets outperform neodymium magnets in high-temperature environments. Neodymium magnets can lose their magnetism if heated beyond their maximum operating temperature unless specifically designed for such conditions.
Durability and Corrosion: Neodymium magnets are prone to corrosion and often require protective coatings. Ferrite magnets, on the other hand, are inherently resistant to rust and corrosion.
Cost Implications: Neodymium magnets are more expensive due to their rare-earth elements. Ferrite magnets are more affordable and widely used in applications where a strong magnetic field is not as critical.
Specific Applications: The choice between neodymium and ferrite magnets largely depends on the application’s specific requirements, including magnetic strength, resistance to heat and corrosion, and budget constraints.
Choosing the Right Magnet for Your Needs
Selecting the right magnet involves considering the application’s specific needs, including the required magnetic strength, exposure to temperatures, environmental conditions, and budget. For those unfamiliar with magnets, the variety of options can be overwhelming. Consulting with a knowledgeable supplier who can offer customized solutions is crucial. Manufacturers like MagnetsTek have the expertise to guide customers in choosing the most appropriate magnets for their applications, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between neodymium magnets and regular ferrite magnets is essential for anyone looking to incorporate magnetic solutions into their projects or products. While neodymium magnets offer unparalleled strength and efficiency, ferrite magnets provide cost-effective solutions for a wide range of applications. Choosing the right magnet depends on a careful assessment of the application’s specific requirements. Consulting with industry experts like MagnetsTek can provide valuable insights and customized solutions, ensuring that you select the best magnet for your needs.